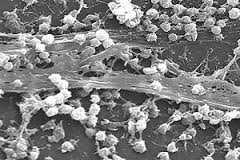
Biofilm is composed of a cluster of microorganisms that adhere to a surface, multiply and secrete a protective matrix. This protective layer will then trap other bacteria, viruses, spores, fungi as well as nutrients and constitute a food reservoir for these organisms but also a protection against various aggressions. Microorganisms will also be able to detach themselves from the biofilm and thus colonize new surfaces.
Where is the Biofilm?
You can find biofilm on all surfaces but especially on all places that come into contact with humans. The hands of a human being are a main vector of propagation of Biofilms (telephones, printers, computer keyboards, door handles, switches, taps, toilet flushes, pens, etc.)
How to limit his training?
In order to limit the formation of biofilm, which becomes more and more resistant over time, it is imperative to set up a cleaning and disinfection plan for the surfaces of the premises. This plan must include a regular schedule of operations in order to avoid the long-term establishment of micro-organisms and their proliferation. The use of a steam cleaner is strongly recommended in the cleaning operation. We recommend our STEAMBIO 3000 or our STEAMBIO 4000 for this operation.


Steps to follow to limit the formation of biofilms or to remove them :
It is strongly recommended that surfaces are cleaned or washed before disinfection, rather than being done at the same time. Indeed, each one has a very specific role:
- cleaning or washing will remove organic, mineral and microbial soiling from the surfaces.
- Disinfection uses a disinfectant to eliminate or inactivate micro-organisms that have not been destroyed by the cleaning-washing phase. Effective products for this purpose include peracetic acid, one of the components of the Bio Apabio product marketed by IBL Specifik.
What is disinfection?
The ANSES (National Agency for Food, Environmental and Occupational Health Safety) also recommends that certain measures be taken to limit microbial concentration. Among these recommendations are the following:
- the design of premises and equipment that comply with hygienic design rules,
- the choice of materials that are wear-resistant and easy to clean and disinfect,
- regular replacement (as soon as they are damaged) of fragile materials,
- minimizing water input, as it promotes microbial growth and can be a vector for contamination.
Where are the best places for the development of biofilms?
A priori, biofilm can settle on a large number of surfaces (except for copper, which is toxic), but it will only succeed in developing if it is not threatened by regular and effective hygiene measures. Thus, in general, it will grow especially in areas that are difficult to access for cleaning and disinfection.
Source: French Food Safety Agency (AFSSA): www.anses.fr
Why is the use of dry steam ideal against biofilms?
The high temperature instantly eliminates allergens and greatly reduces the bacterial load contained in the biofilm. This effect is called "SHOCK" disinfection.
The high temperature instantly destroys the bacterial load. There is no resistance or habituation to steam disinfection as opposed to the use of hygiene products.
The surface-active action of steam makes it a chemical-free detergent and the visual results obtained are unanimously recognised as better than with conventional processes. Steam cleaners have also proven to be effective on hard to reach surfaces such as furniture, beds, stretchers, wheelchairs, sanitary vehicles, etc.
Numerous studies show that steam cleaning methods have unparalleled detergent efficiencies and result in a reduction in the concentration of proteins on the surface of the substrate of approximately 98%.
The application of a "detergent-disinfectant" cleaning does not achieve the same level of efficiency and the percentage of protein concentration reduction is slightly lower (96%).
